Why is this difficult?
Are you struggling to find the right key for your favorite songs on the piano? Many musicians face challenges when songs don't suit their vocal range or skill level.
The Smart Solution
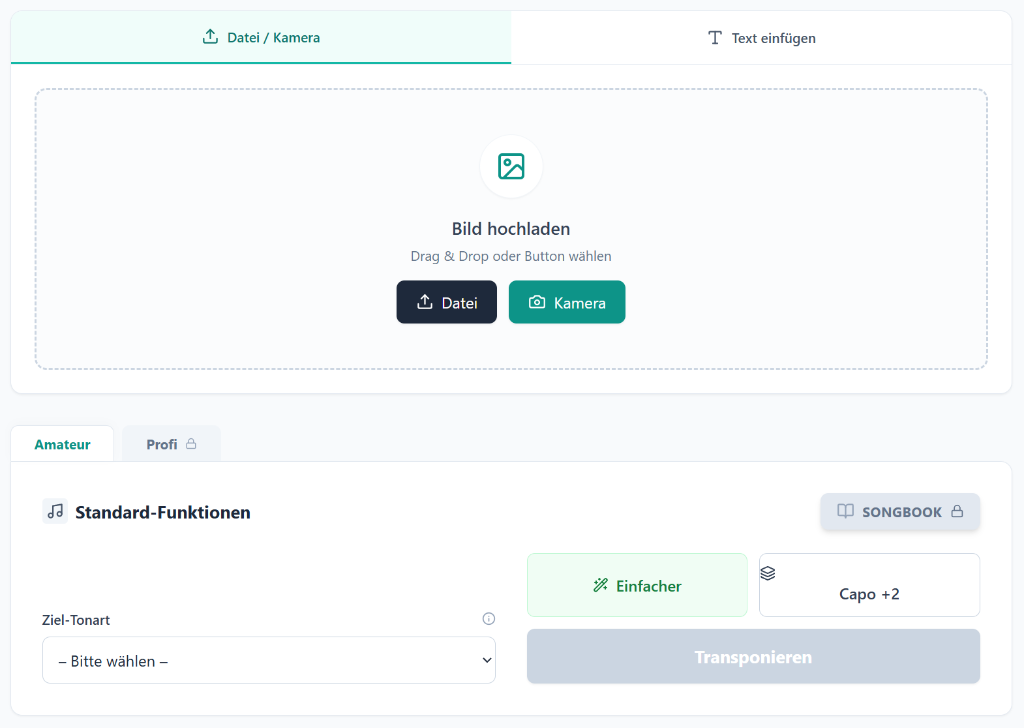
With our tool, you can easily transpose chords for piano, ensuring each song fits your style and ability. Discover how simple it is to adjust the key and make every performance shine.
- User-friendly interface for quick transposition
- Supports a variety of musical styles and genres
- Adjust to any key with just a few clicks
- Perfect for both beginners and seasoned pianists
Easily Transpose Your Piano Chords Online!
Need to play a song but it doesn't sound right? With our 'Transpose chords for piano' tool, you can change the key in seconds, making it suitable for your voice or skill level.
Advanced Theory & Insights
Deepened knowledge for professionals. Analyzing nuances that beginners often miss.
Theoretical Underpinnings of Transposition
Practical Techniques for Efficient Transposition
Transposition and Its Role in Music Composition
FAQ
?
How does transposing chords for piano affect the overall harmonic structure of a piece of music, and what considerations should a pianist take into account when deciding to transpose?
Transposing chords for piano significantly affects the **overall harmonic structure** of a piece by altering its key signature, consequently influencing the mood and emotional impact of the music. Each key has its own **unique character**; for instance, pieces in C major generally feel brighter and more open compared to those in B minor, which may convey a darker quality. As such, transposition can bring a fresh perspective to familiar works, enhancing interpretative possibilities.
When a pianist decides to transpose, there are several **considerations** to take into account:
- Vocal Range: If accompanying a vocalist, it's crucial to transpose to a key that suits their range comfortably.
- Technical Ability: Some keys may present more challenging fingerings and hand positions, particularly with an increase in sharps or flats.
- Harmonic Relationships: Understanding chord relationships, such as **Tonic, Subdominant,** and **Dominant**, is essential to maintain the harmonic integrity of the piece while transposing.
- Instrumental Color: Different keys can affect the timbral qualities of the piano; certain keys may resonate more warmly depending on the instrument.
Ultimately, successful transposition requires both musical intuition and practical skills, allowing the pianist to effectively adapt the music while preserving its essential qualities.
?
Why is understanding the circle of fifths important for pianists when it comes to transposing chords, and how can it aid in the smooth execution of this skill in various musical genres?
Understanding the **circle of fifths** is crucial for pianists when transposing chords because it provides a clear visual representation of the relationships between different keys. This tool not only illustrates the order of sharps and flats but also helps pianists quickly identify the corresponding chords in different keys. For instance, when transposing a song from C major to G major, recognizing that G is a perfect fifth above C allows for a seamless shift in key.
The **circle of fifths** enables pianists to grasp the harmonic structure of a piece, making it easier to maintain the song's emotional quality while adjusting the key. By understanding which chords are diatonically related and how they function within each key, pianists can more confidently transpose various chord progressions. This skill is particularly useful in genres such as jazz and pop, where improvisation and modulation are common.
To improve your transposing abilities, practice playing common chord progressions in different keys using the circle of fifths as a guide. **Start simple**, with familiar songs, and gradually challenge yourself with more complex pieces. This will not only enhance your skill in transposing but also deepen your overall musical understanding.
?
In what contexts might a pianist choose to transpose a chord progression, and how does the choice of key impact the emotional tone and performance practices of a piece?
Transposing a chord progression can serve various practical and creative purposes for a pianist. **Musical directors may instruct a transposition** to suit the vocal range of a singer, ensuring that the piece is comfortable to perform. Additionally, if a pianist is collaborating with other musicians who play in different keys, **transposing** the chords can facilitate smoother ensemble playing.
The choice of key significantly impacts the **emotional tone** of a piece. Each key has its own unique character; for instance, **C major** often conveys brightness and innocence, while **C minor** can evoke melancholy and introspection. Understanding these tonal qualities can help pianists **choose a key** that aligns with their interpretive intentions, tailoring the performance to express specific emotions.
Moreover, different keys can influence **technical execution and performance practices**. Certain keys may place better demands on a pianist's hand positioning and fingerings, making some progressions easier or more fluid to play. Therefore, **experimenting with various keys** during practice can reveal new nuances in the music. When transposing, always listen closely to how the **overall mood and dynamics** shift, ensuring the performance remains cohesive and expressive.
?
How can mastering the technique of transposing chords enhance a pianist's improvisation skills, and what exercises or strategies can be employed to develop this ability?
?
Why do different musical styles or genres often require specific approaches to chord transposition, and how can a pianist adapt their transposing techniques to fit contexts such as jazz, classical, or pop music?
Different musical styles and genres often demand **specific approaches to chord transposition** due to their unique harmonic structures, typical progressions, and stylistic nuances. For instance, in **jazz**, chord progressions frequently include complex extensions, alterations, and substitutions, which necessitate a flexible and inventive approach to transposition. Pianists should focus on understanding **ii-V-I progressions** and think in terms of **voice leading** to maintain the character of the harmony when changing keys.
In contrast, **classical music** tends to adhere to more traditional harmonic practices. Here, transposition involves recognizing the role of **counterpoint and modulation**, often requiring the pianist to maintain the integrity of the original texture while shifting keys. Therefore, awareness of classical forms and the ability to read through varying inversions of chords becomes crucial.
For **pop music**, chord structures are often simpler, typically centered around basic triads. Pianists can enhance their transposing techniques by memorizing common pop progressions (like I-IV-V) and practicing shifting them to different keys using the **circle of fifths**. In all cases, **regular practice** of transposing within each genre will improve flexibility and adaptability, allowing the musician to respond effectively to diverse musical contexts.